!–https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/--
Authorization 上面认证过程,只是确认通信的双方都确认了对方是可信的,可以互相通信。而鉴权是确定请求方有哪些资源权限。API Server目前支持以下几种授权策略(通过API Server的启动参数”–authorization-mode”设置)
AlwaysDeny:表示拒绝所有的请求,一般用于测试 AlwaysAllow:允许接收所有请求,如果集群不需要授权流程,则可以采用该策略 ABAC(Attribute-Based Access Control):基于属性的访问控制,表示使用用户配置的授权规对用户请求进行匹配和控制(老版本中用的,需要配置多个规则,不能及时修改生效,已经淘汰) Webbook:通过调用外部REST服务队用户进行授权 RBAC(Role-Based Access Control):基于角色的访问控制,现行默认规则
RBAC授权模式 RBAC(Role-Based Access Control)基于角色的访问控制,在kubernetes1.5中引入,现行版本称为默认标准。相对其它访问控制方法,拥有以下优势:
对集群中的资源和非资源均拥有完整非覆盖 整个RBAC完全由几个API对象完成,同其它API对象一样,可以用kubectl或API进行操作 可以在运行时进行调整,无需重启API Server
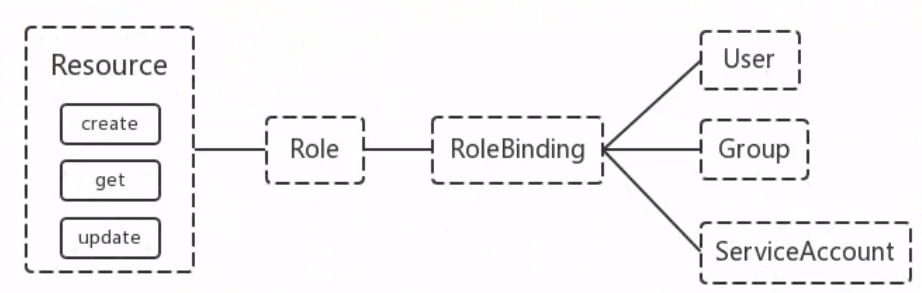
1 RBAC的API资源对象说明 RBAC引入了4个新的顶级资源对象:Role、ClusterRole、RoleBinding、ClusterRoleBinding,4种对象类型均可以通过kubectl与API操作
需要注意的是Kubernetes并不会提供用户管理,那么User、Group、ServiceAccount指定的用户又是从哪里来的呢?kubernetes组件(kubectl、kube-proxy)或是其他自定义的用户在向CA申请证书时,需要提供一个证书请求文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 { "CN" : "admin" , "hosts" : [], "key" : { "algo" : "rsa" , "size" : 2048 }, "names" : [ { "c" : "CN" , "ST" : "HangZhou" , "L" : "XS" , "O" : "system:masters" , "OU" : "System" } ] }
API Server会把客户端证书的CN字段作为User,吧names.O字段作为Group
kubelet使用TLS Bootstraping认证时,API Server可以使用BootStrap token或token authentication file验证=token,无论是哪一种,kubernetes都会为token绑定一个默认的User和Group
Pod使用ServiceAccount认证时,service-account-token中的JWT会保存User信息
有了用户信息,再创建一对角色/角色绑定(集群角色/集群角色绑定)资源对象,就可以完成权限绑定了
Role and ClusterRole 在RBAC API中,Role表示一组规则权限,权限只会增加(累加权限),不存在一个资源一开始就拥有很多权限而通过RBAC对其进行减少的操作;Role可以定义在一个namespace中,如果想要跨namespace则可以创建ClusterRole
Role
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 kind: Role apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1.beta1 metadata: namespace: default name: pod-reader rules: - apiGroups: ["" ] resources: ["pods" ] verbs: ["get" , "watch" , "list" ]
ClusterRole具有与Role相同的权限角色控制能力,不同的是ClusterRole是集群级别的,ClusterRole可以用于:
集群级别的资源控制(例如node访问权限) 非资源型endpoints(例如/healthz访问) 所有命名空间资源控制(例如pods)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 kind: ClusterRole apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: secret-reader rules: - apiGroups: ["" ] resources: ["secrets" ] verbs: ["get" , "watch" , "list" ]
RoleBinding and ClusterRoleBinding RoleBinding可以将角色中定义的权限授予用户或用户组,RoleBinding包含一组权限列表(subjects),权限列表中包含有不同形式的待授予权限资源类型(users,groups,or service accounts);RoleBinding同样包含对被Bind的Role引用;RoleBinding适用于某个命名空间内授权,而ClusterRoleBinding适用于集群范围内的授权
将default命名空间的pod-readerRole授予jane用户,此后Jane用户在default命名空间中将具有pod-reader的权限
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 kind: RoleBinding apiVersioN: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: read-pods namespace: default subjects: - kind: User name: jane apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io roleRef: kind: Role name: pod-reader apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
RoleBinding同样可以引用ClusterRole来对当前namespace内用户、用户组或ServiceAccount进行授权,这种操作允许集群管理员在整个集群内定义一些通用的ClusterRole,然后在不同的namespace中使用RoleBinding来引用
例如,一下RoleBinding引用了一个ClusterRole,这个ClusterRole具有整个集群内对secrets的访问权限;但是其授权用户dave只能访问development空间中的secrets(因为RoleBinding定义在development命名空间)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 kind: RoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: read-secrets namespace: development subjects: - kind: User name: dave apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: secret-reader apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
使用ClusterRoleBinding可以对整个集群中的所有命名空间资源权限进行授权;以下ClusterRoleBinding示例展示了授权manager组内所有用户在全部命名空间中对secrets进行访问
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 kind: ClusterRoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: read-secrets-global subjects: - kind: Group name: manager apiGroup: rbac.authorizatoin.k8s.io roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: secret-reader apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Resources Kubernetes集群内一些资源一般以其名称字符串来表示,这些字符串一般会在API的URL地址中出现;同时某些资源也会包含子资源,例如logs资源就属于pods的子资源,API中URL样例如下:
1 GET /api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/pods/{name}/log
如果要在RBAC授权模型中控制这些子资源的访问权限,可以通过/分隔符来实现,以下是定义一个pod子资源logs访问权限的Role定义样例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 kind: Role apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: namespace: default name: pod-and-pod-logs-reader rules: - apiGroups: ["" ] resources: ["pods" , "pods/log" ] verbs: ["get" , "list" ]
to Subjects RoleBinding和ClusterRoleBinding可以将Role绑定到Subjects;Subjects可以是groups、users或者service account
Subjects中Users使用字符串表示,它可以是一个普通的名字字符串,如“alice”;也可以是email格式的邮箱地址,如“test@163.com ”;甚至是一组字符串形式的数字ID。但是Users的前缀system:是系统保留的,集群管理员应该确保普通用户不会使用这个前缀格式
Groups书写格式与Users相同,都为一个字符串,并且没有特定的格式要求;同样system:前缀为系统保留
实践 创建一个用户只能管理dev空间 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 { "CN" : "devuser" , "hosts" : [], // 这里不写的话表示对所有节点有效? "key" : { "algo" : "rsa" , "size" : 2048 }, "names" : [ { "C" : "CN" , "ST" : "BeiJing" , "L" : "BeiJing" , "O" : "k8s" , "OU" : "System" //这里不能有逗号,不然报错哦 } ] } mkdir cert cd certvim devuser-csr.json wget https://pkg.cfssl.org/R1.2/cfssl_linux-amd64 mv cfssl_linux-amd64 /usr/local /bin/cfssl wget https://pkg.cfssl.org/R1.2/cfssljson_linux-amd64 mv cfssljson_linux-amd64 /usr/local /bin/cfssljson wget https://pkg.cfssl.org/R1.2/cfssl-certinfo_linux-amd64 mv cfssl-certinfo_linux-amd64 /usr/local /bin/cfssl-certinfo chmod a+x /usr/local /bin/cfssl* cd /etc/kubernetes/pki/cfssl gencert -ca=ca.crt -ca-key=ca.key -profile=kubernetes /root/cert/devuser-csr.json | cfssljson -bare devuser export KUBE_APISERVER="https://192.168.128.140:6443" kubectl config set-cluster kubernetes \ --certificate-authority=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/ca.pem \ --embed-certs=true \ --server=${KUBE_APISERVER} \ --kubeconfig=devuser.kubeconfig --certificate-authority=/etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt \ --embed-certs=true \ --server=${KUBE_APISERVER} \ --kubeconfig=devuser.kubeconfig kubectl config set-credentials devuser \ --client-certificate=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/devuser.pem \ --client-key=/etc/kubernetes/ssl/devuser-key.pem \ --embed-certs=true \ --kubeconfig=devuser.kubeconfig --client-certificate=/etc/kubernetes/pki/devuser.pem \ --client-key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/devuser-key.pem \ --embed-certs=true \ --kubeconfig=devuser.kubeconfig kubectl config set-context kubernetes \ --cluster=kubernetes \ --user=devuser \ --namespace=dev \ --kubeconfig=devuser.kubeconfig kubectl create rolebinding devuser-admin-binding --clusterrole=admin --user=devuser --namespace=dev cp -f ./devuser.kubeconfig /root/.kube/config cp -f ./devuser.kubeconfig /home/devuser/.kube/ chown devuser:devuser /home/devuser/.kube/devuser.kubeconfig mv devuser.kubeconfig config kubectl config use-context kubernetes --kubeconfig=devuser.kubeconfig kubectl config use-context kubernetes --kubeconfig=config kubectl run nginx --image=hub.test.com/library/myapp:v1 kubectl get pods